How Many Bitcoins are There? BTC Supply Explained

Disclaimer: The Industry Talk section features insights by crypto industry players and is not a part of the editorial content of Cryptonews.com.
The supply of Bitcoin is fixed, with new BTC tokens entering the market every 10 minutes. But how many Bitcoins are there in 2023?
Currently, 19.4 million, or 92% of the total Bitcoin supply is in circulation, as per CoinMarketCap data.
In this guide, we take a much closer look at the Bitcoin supply, including a full analysis of how it can impact its long-term value.
How Many Total Bitcoins Are There? The Circulating Supply in 2023
To understand the circulating supply of Bitcoin, it is important to go right back to the beginning. Put simply, when Bitcoin was launched in 2009, it was created with a fixed supply mechanism. On average, new BTC tokens enter circulation every 10 minutes.
As we explain in more detail later, the exact block time can vary depending on network conditions. But over the course of time, this has averaged 10-minute cycles. So why does this matter? Well, every time a new block of transactions is confirmed, the circulating supply increases.
Currently, this amounts to 6.25 of newly minted Bitcoin tokens. Previously, however, this stood at 12.5 BTC. And before that, 25 BTC and 50 BTC, respectively. The reason the supply rate changes is due to ‘Bitcoin halving’.

Bitcoin halving happens every 210,000 blocks, or about four years. This reduces the supply of new tokens over time. More specifically, the number of new BTC tokens entering the supply every 10 minutes is reduced by 50%.
The next Bitcoin halving will take place on block number 840,000 – expected in April 2024. Bitcoin halving provides the BTC ecosystem with clarity, certainty, and predictability. After all, Bitcoin cannot suddenly increase its supply.
The Bitcoin supply system is in contrast to traditional currencies, with new money being ‘printed’ at any given time. So, taking all of the above into account, there are currently over 19.4 million Bitcoins in circulation right now. This amounts to approximately 92% of the total supply.
Once the supply hits 100%, there will be 21 million BTC tokens in circulation. Based on halving cycles of 210,000 blocks, Bitcoin is expected to reach its maximum supply in 2140, as per the Blockchain Council.
Still asking the question: How many Bitcoins are there in total? One of the easiest ways to find this information is on CoinMarketCap. The data aggregation platform updates in real-time allowing users to gain insights on how many people use Bitcoin in 2023. This enables people to establish how many Bitcoins are there in the world.
Key Calculations: How Many Bitcoins Are There Left to Mine?
While third-party platforms like CoinMarketCap make it simple to keep tabs on Bitcoin’s supply – seasoned investors prefer to do their own calculations. This removes the need to trust the information being provided by another source.
In order to reach a conclusive calculation, it is important to understand how the supply of Bitcoin is determined.
Let’s start with the Bitcoin mining system.
Bitcoin Mining – Keeping the Network Decentralized
Wondering how many Bitcoins are there left to mine? Considering that 19.42 million tokens are already in circulation, this leaves approximately 1.58 million BTC left to mine.
One of the many unique features of Bitcoin is its decentralized status. This means that, unlike traditional currencies, the Bitcoin network is not controlled by a central bank or government. Moreover, Bitcoin transactions do not require third-party authorization.
This is also in contrast to traditional currencies, which must go through banks and other intermediaries when being transferred. Bitcoin transactions are instead verified by blockchain miners. To ensure that Bitcoin is an inclusive financial system, anyone can help mine transactions.
- The process requires miners to connect hardware to a device.
- The device will attempt to solve a cryptographic equation
- The equation is so complex that only a specialist device can solve it.
- Moreover, it takes about 10 minutes on average for the equation to be solved.
Not only does mining require expensive, powerful hardware – but the process consumes a considerable amount of electricity. This is because of the complexity of the cryptographic equation that needs to be solved.
For example, the New York Times reports that Bitcoin mining uses more energy than entire countries. The same article states that the average household would require 9 years’ worth of energy supply just to mine a single Bitcoin block.
Although the Bitcoin mining system is inclusive, it is very competitive. The reason for this is that the miner successfully verifying the block receives newly minted Bitcoin. This currently amounts to 6.25 BTC for every mined block.
Therefore, based on current Bitcoin prices, miners receive $187,500 worth of BTC tokens every 10 minutes. This huge incentivization is why Bitcoin miners are prepared to invest so much into the process.
And, as more miners enter the market, this increases the difficulty of each cryptographic equation. In turn, only the most powerful mining devices and those with access to cheap electricity have a realistic chance of being successful.
Although Bitcoin mining is now dominated by large-scale operations, there are still ways for the average citizen to get involved. Cloud mining companies, for example, pool resources from multiple small investors to collectively mine Bitcoin. That said, not only are cloud mining pools highly centralized but many are scams.
Ensuring Bitcoin Inflation Rates Cannot be Manipulated
Investors should also understand inflationary controls when asking the question: How many Bitcoins are there?
This is a major concern with traditional currencies. After all, no longer are currencies backed by gold or other valuable assets. Instead, central banks are free to print as much money as they wish.
- For example, the US Federal Reserve printed over $3 trillion worth of US dollars in 2020. This was in response to COVID-19 measures and amounted to almost one-fifth of the total supply.
- Similarly, the Spectator notes that in 2020, the Bank of England printed almost £500 billion throughout the pandemic.
- The European Central Bank also engaged in ‘money printing’ during the pandemic, amounting to €1.85 trillion.
This trend can be found in most corners of the world. So why does this matter, and how does it relate to the Bitcoin supply?
Well, while the underlying reasons can vary, ‘currency printing’ has one common factor; it increases the supply of money and reduces its value. This is because of the impact of inflation, which increases the cost of living.

And when too much money enters circulation at any given time, this can have a disastrous impact on the economy.
These risks are not present in the Bitcoin network. This is because the new supply of Bitcoin tokens entering circulation is fixed. Most importantly, the supply rate is built into the Bitcoin code, and it cannot be amended. This means that the Bitcoin supply is fixed and consistent.
Bitcoin Halving Every 210,000 Blocks
Just like traditional currencies, Bitcoin currently experiences inflation. However, as noted above, inflation is fixed and predictable.
Inflation arises when new BTC tokens enter circulation. As we have established, this happens every time a new block is mined, approximately in 10-minute cycles.
Crucially, however, the amount of new Bitcoin entering circulation is reduced by 50% for every 210,000 blocks mined. This is known as the Bitcoin halving event, and it takes place approximately every four years.
- Originally, the Bitcoin block reward was 50 BTC.
- After 210,000 blocks were mined in November 2012, the mining reward was reduced to 25 BTC.
- Then, in July 2016 – after 420,000 blocks, the reward was reduced to 12.5 BTC.
- The most recent Bitcoin halving event took place in May 2020 – after 630,000 blocks were mined. This reduced the mining reward to just 6.25 BTC.
- The next Bitcoin halving is scheduled on block 840,000, expected in April 2024. This will reduce the mining reward to 3.125 BTC.
Bitcoin halvings will continue every 210,000 blocks until the total supply reaches 21 million. As noted earlier, this is expected to happen in 2140. Once the maximum supply is reached, there will not be any new BTC tokens entering circulation.
In other words, Bitcoin will no longer be an inflationary asset.
| Halving Event | Date | No. Blocks | New BTC Per Block | Total New BTC Tokens |
| 0 | Jan 2009 | 0 | 50 | 0 |
| 1 | Nov 2012 | 210,000 | 25 | 10,500,000 |
| 2 | Jul 2016 | 420,000 | 12.5 | 5,250,000 |
| 3 | May 2020 | 630,000 | 6.25 | 2,625,000 |
| 4 | April 2024 | 840,000 | 3.125 | 1,312,500 |
| 5 | Approximately 2028 | 1,050,000 | 1.5625 | 656,250 |
| 6 | Approximately 2032 | 1,260,000 | 0.78125 | 328,125 |
| 7 | Approximately 2036 | 1,470,000 | 0.390625 | 164,063 |
| 8 | Approximately 2040 | 1,680,000 | 0.1953125 | 82,031 |
The above table shows how quickly the supply of new Bitcoin tokens reduces over time. For example, once the 10th Bitcoin halving happens in approximately 2048, only 0.048828125 BTC will enter the supply after each block.
This is an innovative system and one of the core reasons why Bitcoin is the best cryptocurrency to buy.
Key Figures: How Many Total Bitcoins Are There?
So now that we have explained how the underlying network determines supply, let’s summarize the question: How many Bitcoins are there?
| How Many Bitcoins Are There in Circulation? | 19,418,512 BTC |
| How Many Bitcoins Are Out There to Mine? | 1,581,488 BTC |
| Percentage of Bitcoins in Circulation | 92.47% |
| Percentage of Bitcoin Supply Left to Mine | 7.53% |
| Percentage of Bitcoin Dominance | 49.4% |
| 24-Hour Trading Volume | $10.9 billion |
The above table is based on figures at the time of writing. The new supply of Bitcoin will increase approximately every 10 minutes. This will have an impact on the percentage of BTC tokens still left to mine.
How Many BTC Tokens Can There be at the Same Time?
The number of Bitcoins in circulation will continue to increase after each block is mined.
As noted above, this happens approximately every 10 minutes, with 6.25 BTC entering circulation. This increase will continue over the course of time until Bitcoin reaches its maximum supply of 21 million tokens.
When this happens, the supply of Bitcoin will not increase further. This means that Bitcoin miners will no longer be rewarded with newly minted tokens. Instead, they will only receive transaction fees that were paid for the respective block being mined. More on this later.
Another point to note is that when Bitcoin reaches its maximum supply, it will theoretically become a deflationary currency. This is because the supply will actually decrease if BTC tokens become unrecoverable.
For example, if tokens are transferred to an incorrect wallet address. Or, if the investor forgets the password to their wallet and no longer has access to the backup passphrase.
What Percentage of the Bitcoin Supply is Due to Mining
When the first Bitcoin block was mined on January 3rd, 2009, the circulating supply was just 50 BTC. This was known as the Genesis Block, or Block 0, as explained by Blockchain.com.
Thereon, approximately every 10 minutes, new BTC tokens entered circulation. After each new block, miners received a reward. This will continue to be the case until Bitcoins supply reaches 21 million tokens.
So that begs the question: Are all Bitcoins in circulation a result of mining? The simple answer is yes. In other words, Bitcoin can only enter circulation once a new block has been mined. This is built into the Bitcoin code, and it ensures the supply is fair, transparent, and fixed.
We mentioned above that the current circulating supply of Bitcoin is 19,418,512 BTC. This figure also refers to the number of Bitcoins that have been mined. As such, 100% of Bitcoin tokens in circulation were originally distributed to miners.
In turn, the general public can only buy Bitcoin once the newly mined tokens are sold. Miners must sell their Bitcoin at some point, as they are in business to make money. And the only way to realize their mining profits is to sell their Bitcoin on the open market.
If the miner has sufficient resources, they might look to sell their Bitcoin at strategic intervals. This means that they might not sell their Bitcoin until prices are sufficient.
How Does the Supply and Demand of Bitcoin Work?
Experienced crypto traders will focus strongly on the supply and demand of Bitcoin. This is much the same as any asset class, especially commodities like gold, silver, and oil. After all, the supply and demand of an asset will play a role in its market value.
- For example, if OPEC announces that it will increase daily production levels, then this will have a negative impact on the value of oil. This is because there is more oil in the circulating supply.
- And when OPEC announces a reduction in production levels, this will positively impact the price of oil.
- However, this is on the proviso that demand for oil stays the same.
However, in the world of Bitcoin, things work slightly differently. This is because the supply of Bitcoin is not determined by policymakers. Nor can it be manipulated by central banks or governments.
On the contrary, the supply of Bitcoin remains constant. As we have established, new Bitcoins enter circulation every time a new block is mined. And on average, this happens approximately every 10 minutes. As a decentralized and immutable system, this will never change.
This enables traders to make informed decisions based on a predictable supply model. But what about demand? Well, demand for Bitcoin is determined by market forces. This is much the same as stocks, commodities, currencies, and other assets.
Let’s take a much closer look at how the demand and supply of Bitcoin is influenced.
Broader Market Cycles
Historically, Bitcoin operates in prolonged bull and bear cycles.
When Bitcoin rises in value over longer periods of time, this increases market sentiment. In turn, this motivates more people to buy Bitcoin, as price increases are attractive to investors. This is otherwise referred to as fear of missing out (FOMO).
But when Bitcoin enters a prolonged bear market, there are fewer people willing to buy it. This is because of continued declining prices. And when market prices drop rapidly, people panic sell. This can increase the speed that the Bitcoin price declines.
Bitcoin Halving Events
Bitcoin halving is an important event for investors to keep tabs on.
When the Bitcoin mining reward is halved, this slows down the rate of inflation. This is because for each 10-minute block that is mined, 50% fewer tokens enter circulation.
For example, when the next Bitcoin halving event takes place in 2024, the mining reward will reduce from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC.
- This links back to the example we gave earlier, where oil prices increase when OPEC reduces its daily production output.
- This is because the demand for oil remains constant.
- But if there is less oil in the market, people are willing to pay more for it.
Going back to Bitcoin, the halving event follows a similar concept. This is supported by Bitcoin’s price action after its prior three halvings.
According to CoinMarketCap data, Bitcoin was valued at $9,100 on May 11th, 2020. This was the date of Bitcoin’s previous halving event, where the mining reward was reduced from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC. 17 months after the halving event, Bitcoin peaked at over $68,000. This translates to an increase of over 650%.
Similar events took place during the 2016 Bitcoin halving. On July 9th, 2016, Bitcoin was worth $662. 17 months later, Bitcoin peaked at a then-all-time high of $20,000. This amounts to post-halving gains of over $2,900.
Therefore, history suggests that demand for Bitcoin increases in response to the halving event. And because there is less Bitcoin entering the market, this has resulted in prolonged price appreciation.
Not only does Bitcoin benefit from its halving event but some of the best new cryptocurrencies too.
Fundamental News
Fundamental news also has an impact on the demand for Bitcoin. This is much the same as traditional stocks.
For example, consider a pharmaceutical company that has a new vaccine approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The market will respond positively to this news, meaning more investors are motivated to buy shares in the pharmaceutical company.
- Now consider how the markets would react if the SEC approves a Bitcoin ETF application.
- As reported by Reuters, the SEC has declined dozens of Bitcoin ETF applications to date.
- But many analysts believe it is only a matter of time before the first Bitcoin ETF gets the green light.
- If and when this happens, this would be a major milestone for Bitcoin and potentially increase demand from institutional investors.
Another area that can influence the demand for Bitcoin is regulation. For example, if a country bans Bitcoin outright, this could reduce demand on a much broader scale.
But if a major economy were to recognize Bitcoin as legal tender, demand would increase significantly. This is because Bitcoin would be treated the very same as the country’s domestic currency.
Demand for Bitcoin in the Trading Markets
Investors will also look at the Bitcoin trading markets to evaluate current demand levels. A good starting point is to look at daily trading volumes. History suggests that when Bitcoin is in a bullish run, daily trading volumes increase. This is because more people are looking to buy Bitcoin.
And when Bitcoin is in a bearish cycle, trading volumes decrease. This is because there is less interest in Bitcoin.
We mentioned earlier that over the prior 24 hours, $10.9 billion worth of Bitcoin has been traded across crypto exchanges. This is 84% lower than the $68.3 billion daily trading Bitcoin witnessed in early 2021, as reported by Reuters.
Another metric to look at is the market capitalization. This metric looks at the total value of Bitcoin multiplied by the number of tokens in circulation.
- For example, there are currently 19,418,512 BTC in circulation, and current BTC/USD prices amount to just over $30,000.
- This means that Bitcoin currently has a market capitalization of $595.1 billion.
However, just like the daily trading volume, the market capitalization of Bitcoin is much lower when compared to its 2021 bull run. At its peak in November 2021, Bitcoin surpassed a market capitalization of over $1.2 trillion.
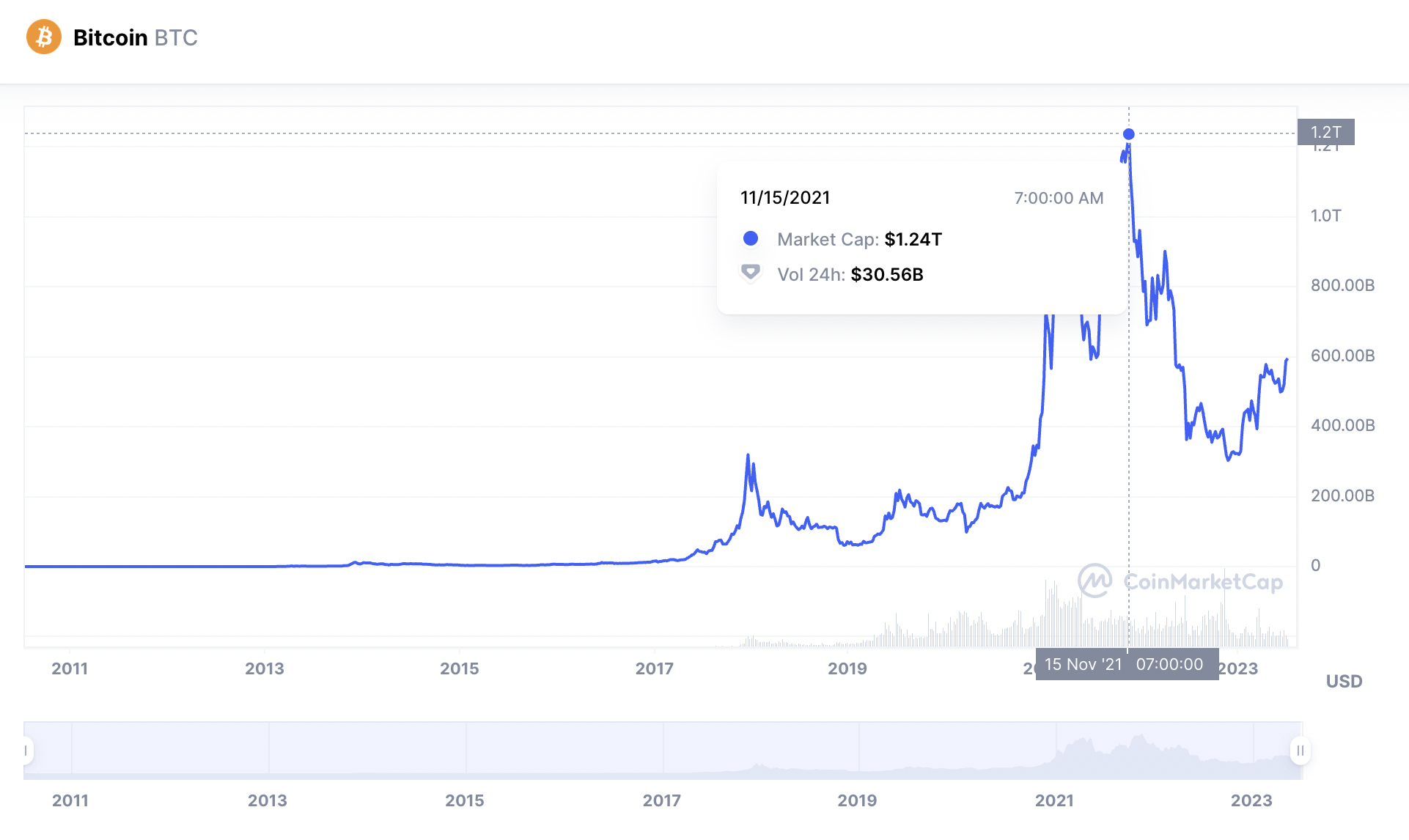
This is just over 100% more than Bitcoin’s current valuation. Once again, this is due to lower demand for Bitcoin, as per the broader bear market.
With the next Bitcoin halving expected for April 2024, demand for Bitcoin could soon enter an upward trend. In addition to Bitcoin, some of the best altcoins could also follow suit. This is because when Bitcoin appreciates, so does the broader crypto market. Check out our guide on the best crypto to buy during the bear market.
Do Unrecoverable Bitcoins Impact the Supply?
We have established that the supply of Bitcoin is fixed and immutable. To reiterate, the supply will increase every time a new Bitcoin block is mined. And this will happen approximately every 10 minutes until the maximum supply of 21 million tokens is reached.
However, investors should recognize that not all Bitcoins in circulation are accessible. This is because some Bitcoins are deemed unrecoverable.
- For example, consider the consequences of storing Bitcoin in a non-custodial wallet and forgetting the password.
- The simple solution is to recover the wallet via its backup passphrase.
However, what happens if the backup passphrase has since been lost?
- In this scenario, it is highly unlikely that the Bitcoins can be recovered.
- This is because of the decentralized nature of the Bitcoin blockchain.
- More specifically, there is no intermediary that can help recover the Bitcoin wallet.
- And hence, some would argue that these Bitcoins should no longer be considered in the overall supply.
One of the most infamous cases to consider is Stefan Thomas.
- According to a New York Times article, Thomas was paid 7,002 BTC in 2011 for creating a video about how cryptocurrencies work.
Back then, Bitcoin was trading at around $5 per token and was barely known outside of the programming world. - Thomas stored the 7,002 BTC in a private wallet that he no longer has the password to.
- This means that the Bitcoin is no longer recoverable.
- At its peak, the 7,002 BTC would have been worth over $476 million.
Crucially, because the 7,002 BTC tokens cannot be recovered, they are technically no longer in the circulating supply. And when the supply is reduced and demand remains steady, this can increase the price of Bitcoin.

This is much the same as a traditional share buyback scheme. The company will use its own working capital to buy its shares from the open market. And removing the shares from the circulating supply increases their value.
According to the Blockchain Council, 4 million Bitcoins have been lost from the circulating supply. This reduces the Bitcoin supply from 21 million down to 17 million.
However, this doesn’t include the estimated 1 million Bitcoin tokens held by Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin. These tokens have remained idle in a Bitcoin wallet since 2010. More than 13 years have since passed, so many argue that they should no longer be included in the circulating supply.
Stolen Bitcoins
And then there’s the question of stolen Bitcoins. On the one hand, stolen Bitcoins are usually laundered before being cashed out. However, this is increasingly becoming more difficult due to improvements in blockchain forensics.
After all, Bitcoin transactions are posted to the public ledger. If stolen Bitcoins are moved from an identified wallet, law enforcement agencies can be notified in real-time. This increases the risk of detection, so criminals will often leave the stolen Bitcoins sitting idle in the wallet.
For example, consider the case of the 2011 Mt. Gox hack. The wallet address listed below has been identified as belonging to the hacker.
1FeexV6bAHb8ybZjqQMjJrcCrHGW9sb6uF
It is one of the largest Bitcoin wallets in existence, with over 80,000 BTC. This values the wallet at almost $2.5 billion, based on current Bitcoin prices. However, the tokens have remained idle since 2011.
As such, in cases such as this, some would argue that the 80,000 BTC tokens should not be included in the circulating supply.
Ultimately, the risk of Bitcoins being lost or stolen will likely never go away. This means that when Bitcoin reaches its maximum supply, it will become a deflationary asset.
This is because no new tokens will enter the market. But the supply will decline as each case of lost or stolen tokens emerges.
Who Owns the Most BTC Tokens?
The transparent nature of the blockchain means that wallet balances are public information.
According to BitInfoCharts, the largest Bitcoin wallet has over 248,000 BTC. This belongs to Binance and is valued at over $7.6 billion. Bitfinix has the second-largest Bitcoin wallet, holding over 178,000 BTC and valued at more than $5.4 billion.
These two wallets alone amount to over 2% of the total Bitcoin supply. The third largest Bitcoin wallet address is owned by an unknown person or entity. This holds over 118,000 BTC and is valued at $3.6 billion.
BitInfoCharts also states that there are 5,789 Bitcoin wallets valued at least $10 million. This is compared to over 40 million wallets holding between $1 and $100 worth of Bitcoin.
How Much Money has Bitcoin Made for Investors?
Early adopters of Bitcoin have generated life-changing returns.
For example, the earliest recorded price of Bitcoin is $0.06, according to CoinMarketCap data. Since then, Bitcoin has hit an all-time high of over $68,000. This translates to growth of over 113 million percent.
Moreover, those mining Bitcoin in its early days would have yielded 50 BTC for each block mined. Based on its all-time high, that 50 BTC would have been worth $3.4 million. Bitcoin mining was a lot easier before the network became mainstream.
As such, people could successfully mine blocks with a standard desktop computer and graphics processing unit (GPU).
That being said, it’s not just early adopters that have done incredibly well from Bitcoin’s growth. For example, those buying Bitcoin in December 2018 would have paid just $3,500 per BTC. The price of Bitcoin has since grown by over 1,842%.
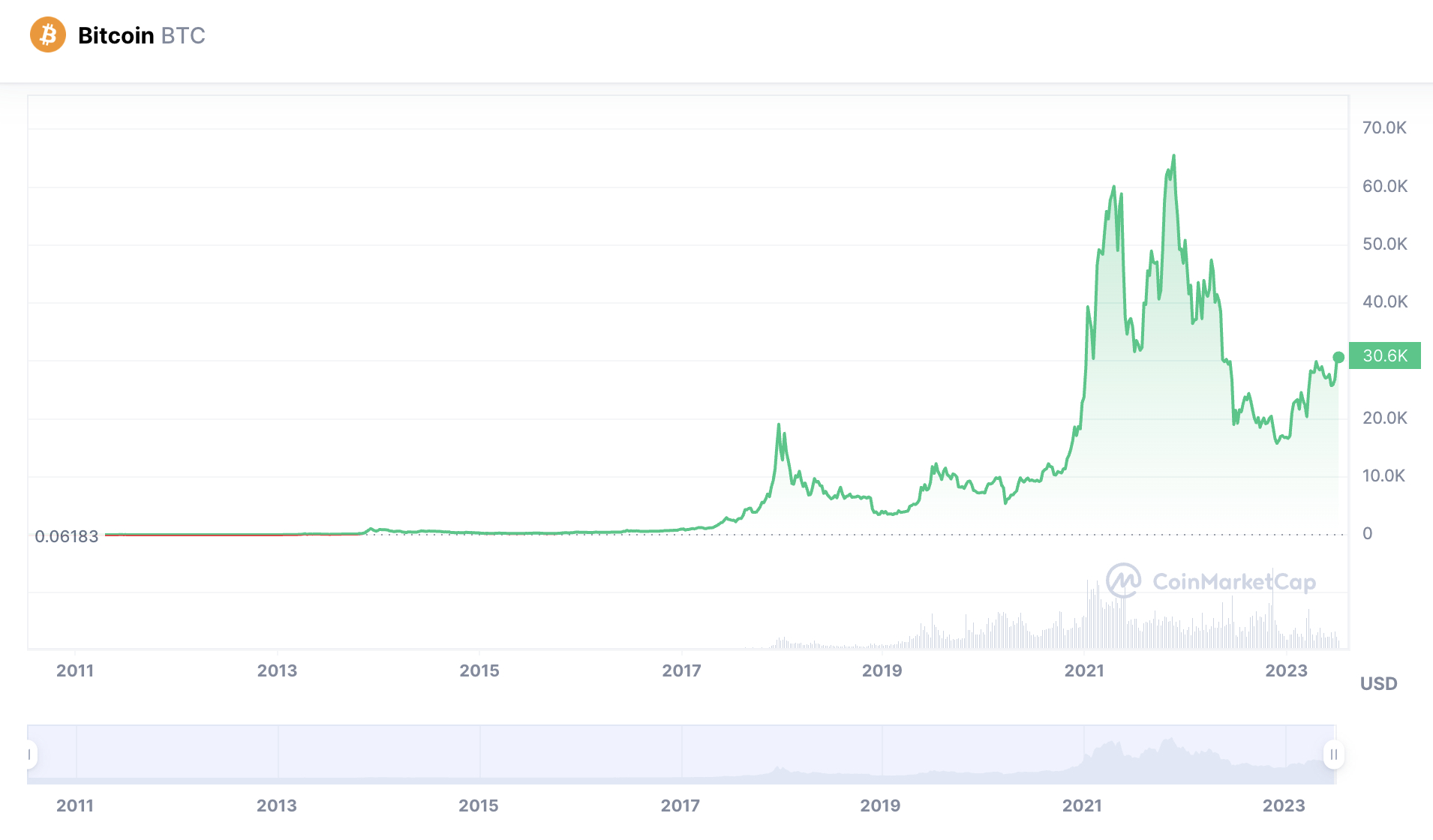
Similarly, Bitcoin declined to lows of just over $5,000 in early 2020. Based on its all-time high, Bitcoin has since increased by over 1,200%.
Crucially, long-term investors have historically done well. This is especially the case for those buying Bitcoin when the markets are bearish. This is because Bitcoin can be purchased at a lower price when compared to its prior peak.
For example, Bitcoin is currently trading at $30,000. This is 55% below its former all-time high. For many, this makes it an attractive time to buy Bitcoin.
- On the flip side, those that sell Bitcoin when prices are falling often do so at a loss.
- For example, consider an investor buying Bitcoin when it peaked at $20,000 in late 2017.
- 12 months later, Bitcoin was worth just $3,500.
- This represents a loss of over 80%.
- However, those that held on for another 35 months would have seen Bitcoin surpass $68,000.
- From an entry price of $20,000, that’s growth of 240%.
Ultimately, investors should prepare themselves for plenty of volatility when investing in Bitcoin.
Were All Bitcoins Mined?
The only way that new Bitcoin enters circulation is via mining. There is no other way for Bitcoin to be created. This means that all 19.4 million BTC tokens currently in circulation were mined.
But this will all change once Bitcoin hits 21 million tokens. We explain the consequence of Bitcoin reaching its maximum supply in the following section.
What Happens When Bitcoin Reaches 21 Million Tokens?
The supply of Bitcoin will continue to increase after each block of transactions is verified. This happens approximately every 10 minutes. It is estimated that Bitcoin will reach its maximum supply of 21 million tokens in the year 2140.
When the maximum supply is reached, miners will no longer receive new BTC tokens as a reward. So what will happen to miners if there is no longer any incentivization?
As noted in the Bitcoin whitepaper, miners will still be motivated to verify transactions and keep the network safe. This is because miners will continue receiving transaction fees after verifying a block.
The theory is that Bitcoin will be worth significantly more once it hits its maximum supply. In turn, the amount of fees received for each block of transactions will have also increased.
Transaction fees also increase when the Bitcoin markets are bullish. This is because there are more people trading Bitcoin, meaning more transactions. And when the number of transactions increases, fees also rise.
So how much do Bitcoin miners currently earn from transaction fees alone?
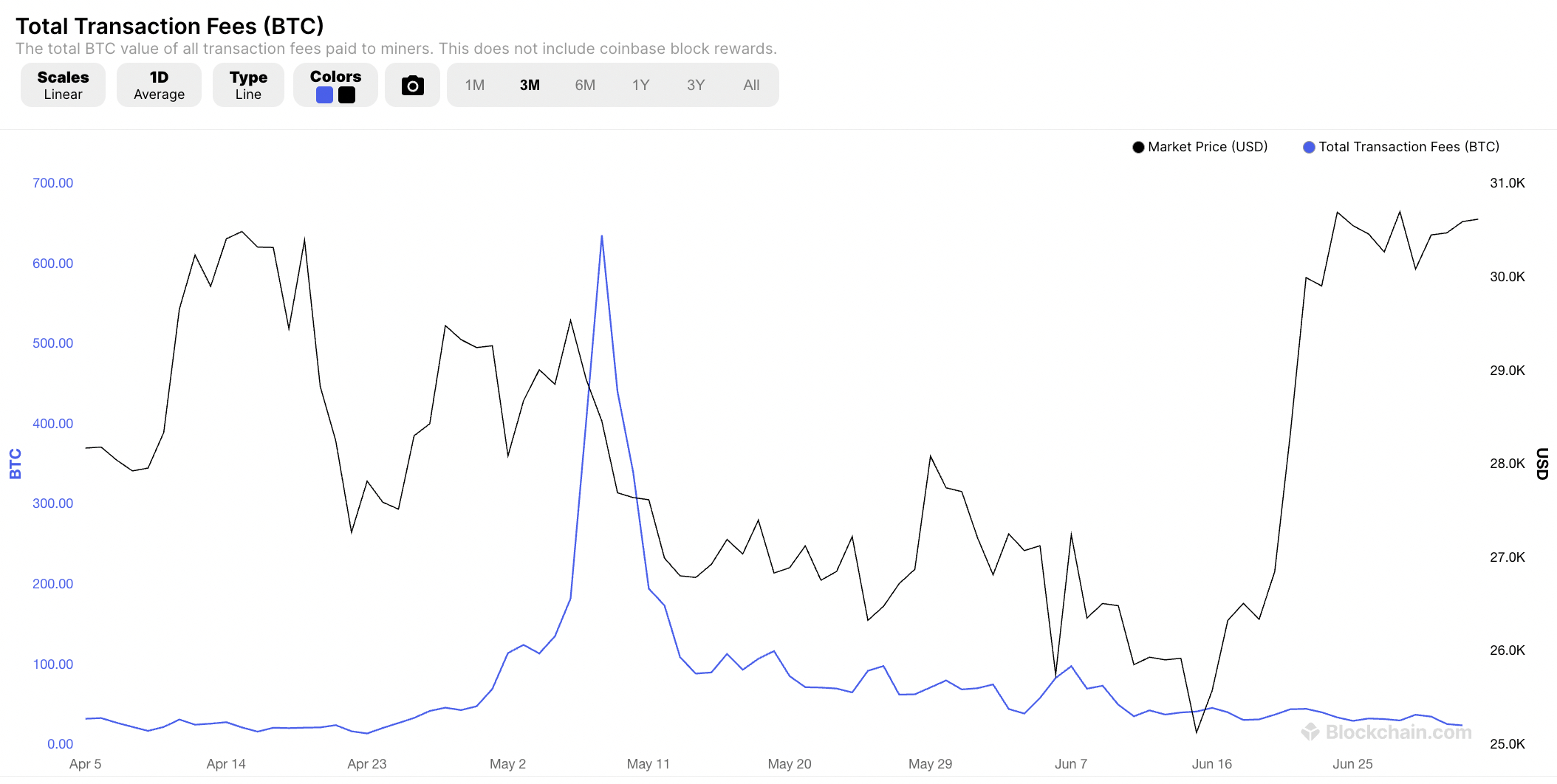
According to Blockchain.com, nearly 24 BTC was paid in transaction fees over the prior 24 hours. Based on current Bitcoin prices of $30,000, this amounts to $720,000 in revenue. Considering the average block time of 10 minutes, that’s just $5,000 per verified block.
This figure fluctuates widely, though. For example, three weeks prior, daily transaction fees amounted to 97 BTC. This increases the daily revenue to over $2.9 million.
As recently as May 8th, 2023, more than 635 BTC was paid in daily transaction fees. On this day, Bitcoin was trading at $28,400. This means that daily transaction fees amounted to over $18 million, or $125,000 per 10-minute block.
Another thing to remember is that when Bitcoin reaches 21 million tokens, the supply will be at its highest. Not only that, but the supply of Bitcoin will reduce as more tokens become lost. Ultimately, should the demand remain consistent, the price of Bitcoin could increase indefinitely.
The Verdict
In summary, we have explored the question – how many BTC are there? While 19.4 million BTC tokens are in circulation, it is estimated that 20% is no longer recoverable.
This means that the actual supply is potentially much lower. To keep tabs on the supply of Bitcoin, CoinMarketCap provides real-time figures.
References
https://coinmarketcap.com/currencies/bitcoin/
https://ycharts.com/indicators/bitcoin_average_confirmation_time
https://www.blockchain-council.org/cryptocurrency/how-many-bitcoins-are-left/
https://www.zenledger.io/blog/bitcoin-halving/
https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/09/03/climate/bitcoin-carbon-footprint-electricity.html
https://www.cityam.com/almost-a-fifth-of-all-us-dollars-were-created-this-year/
https://www.spectator.co.uk/article/mervyn-king-needless-money-printing-fuelled-inflation/
https://www.nytimes.com/2020/12/10/business/european-central-bank-stimulus-coronavirus.html
https://www.blockchain.com/explorer/blocks/btc/000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f
https://www.tradingview.com/symbols/BTCUSD/
https://www.opec.org/
https://www.tradingview.com/symbols/BTCUSD/
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-crypto-currency-idUSKBN29A1N6
https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/12/technology/bitcoin-passwords-wallets-fortunes.html
https://www.blockchain.com/explorer/addresses/btc/1FeexV6bAHb8ybZjqQMjJrcCrHGW9sb6uF
https://bitinfocharts.com/top-100-richest-bitcoin-addresses.html
https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
https://www.blockchain.com/explorer/charts/transaction-fees
https://blog.chainalysis.com/reports/bitcoin-addresses/
FAQs
How many people have 1 BTC?
According to BitInfoCharts, more than 1 million Bitcoin wallets hold at least 1 BTC.
How many BTC addresses are there?
A recent Chainalysis study found that more than 460 million BTC addresses have been created, although many of these are not “economically relevant”.
What happens to miners after all Bitcoins are mined?
Once Bitcoin reaches its maximum supply of 21 million tokens, miners will only earn transaction fees.
How many types of Bitcoins are there?
Bitcoin is a fungible asset, meaning there is only one type of BTC token.
Is there 2 million Bitcoin left to mine?
According to CoinMarketCap data, there are just over 1.58 million Bitcoins left to mine.
How many Bitcoins are there right now?
Out of its maximum supply of 21 million BTC tokens, 19.4 million BTC tokens are in circulation.



